High Temperature Hydrogen Attack (HTHA) is a condition that can occur in process equipment exposed to hydrogen at elevated temperatures and pressures over time. Hydrogen reacts with carbides in steel and can manifest into internal decarburization and fissuring including molecular hydrogen and methane accumulating at grain boundaries.
Subsequent high localized stresses can lead to formation of fissures or cracking in steel, resulting in degradation of mechanical properties. HTHA poses a substantial threat of catastrophic failure if left undetected. The main factors influencing HTHA are hydrogen partial pressure, temperature, the duration of the exposure, and stress. Carbon and low alloy steels are the most susceptible to HTHA but any process piping and vessels with the above combination are at risk.
Throughout the industry, conventional methodologies have not proven effective at detecting early-stage High-Temperature Hydrogen Attack (HTHA). TechCorr has recognized this limitation and has adopted a suite of advanced NDE screening methodologies that employ the latest in advanced ultrasonic equipment and techniques to accurately diagnose symptoms of HTHA:
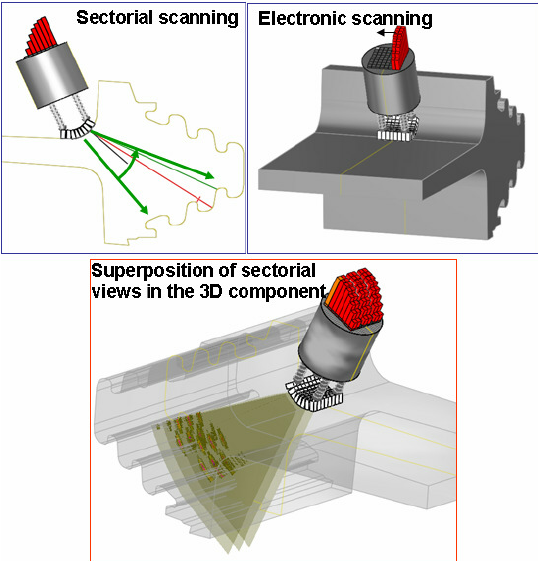
64 ELEMENT PAUT - High Resolution Phased Array
- Increased Resolution: Sound is generated across the active elements when a voltage is applied. With increased firing power/elements, a greater resolution is achieved.
- Detailed Detection: Greater resolution allows for the detection of smaller indications that may not be identified using conventional ultrasonic methods, and the ability to discriminate between single or clusters of smaller indications.
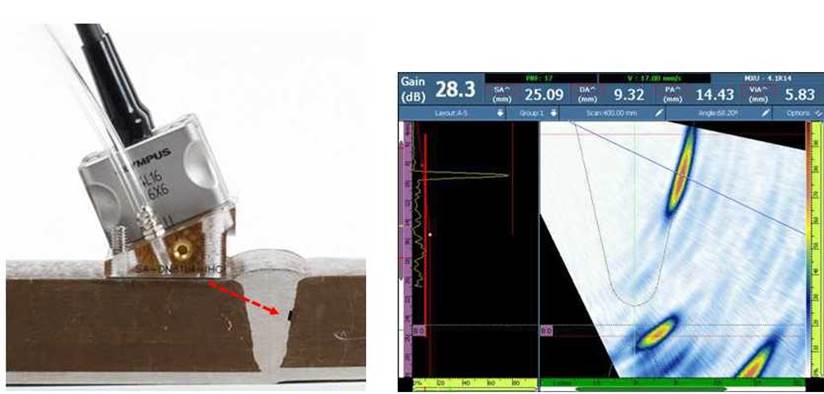
TOFD - Time Of Flight Diffraction
- High Sensitivity: A diffraction-based method that measures the reflection of the indication body and diffraction of the sound wave at the indication tips, making it a highly sensitive sizing technique.
- Reliable Screening: A reliable tool for early-stage HTHA detection.
- Wide Coverage: Useful for examining welds and parent materials, offering a wide coverage area.
- Efficiency: Small data files and readily available, cost-effective equipment.
- Complementary: Needs to be performed in conjunction with other NDE methods to verify exact position and indication type.
TULA - TOFD Ultra Low Angle
- High Sensitivity: A simple yet highly sensitive method for detecting HTHA.
- Fast Scanning: Scan speeds exceed those of Phased Array and TFM.
- Specific Focal Depths: Probes with different specific focal depths.
- Flexible Application: Can be used in place of TOFD where there is only room for one probe.
- Essential Training: Operator training is essential for effective use.
TFM - Total Focus Method
- Comprehensive Detection: Similar to PAUT, but with one element firing and all elements listening for reflections.
- Versatile Orientation: Detects defects in many different orientations.
- High Sensitivity: Good sensitivity to even small defects.
- Data Management: Generates very large data files.
- Methodical Process: A slower method compared to TOFD and TULA.
TechCorr’s adoption of these advanced screening methodologies ensures accurate detection and assessment of HTHA, providing you with reliable data to make informed maintenance and safety decisions.