Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
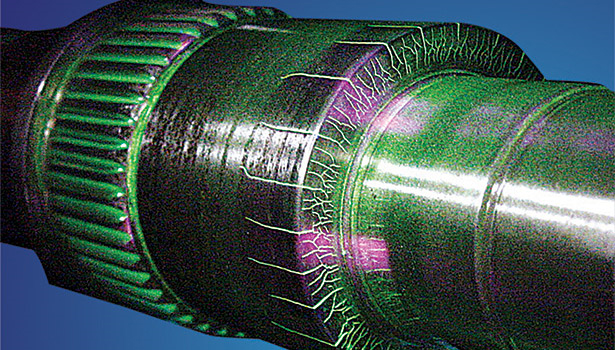
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT), also known as Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI), stands as a pivotal non-destructive testing (NDT) technique, specifically designed for the detection of surface and shallow subsurface defects in ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, cobalt, and their alloys.
The methodology involves inducing a magnetic field within the material, achieved either through direct or indirect magnetization. Direct magnetization occurs by passing an electric current through the test object, generating a magnetic field within it. Conversely, indirect magnetization entails applying a magnetic field externally to the test object, without passing an electric current through it. The magnetic lines of force, perpendicular to the direction of the electric current (which can be alternating current - AC, or rectified AC - DC), facilitate the identification of defects.
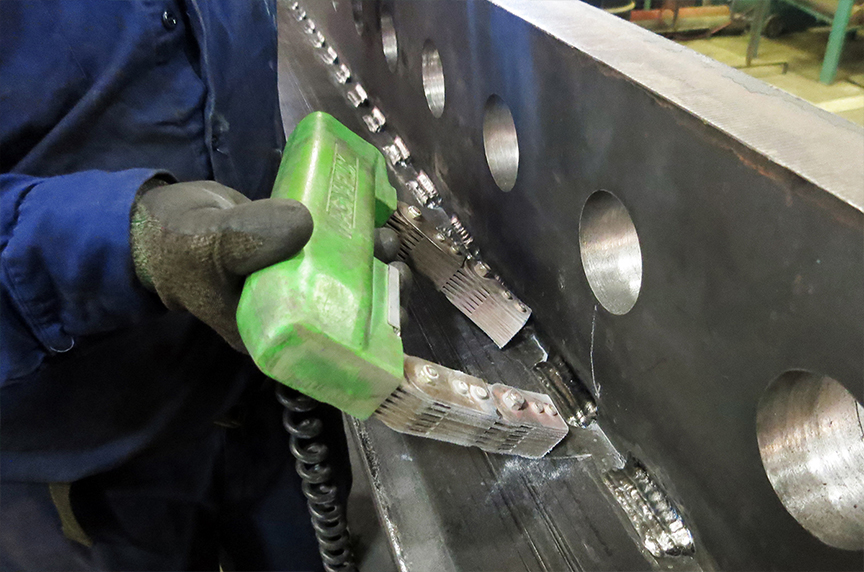
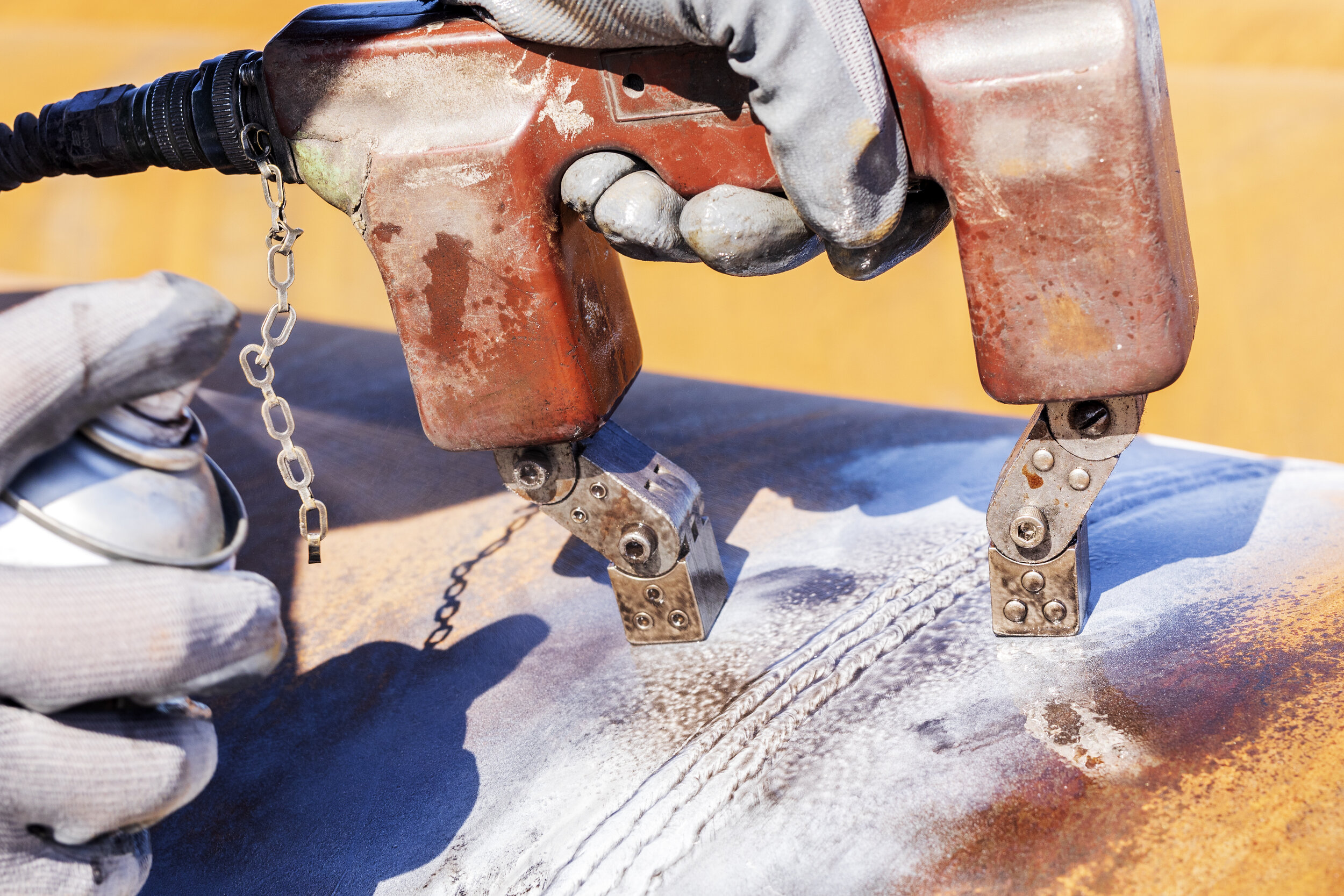
TechCorr employs Dry Powder and Wet Fluorescent Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) variants, offering versatility in detecting surface and near-surface discontinuities. This technique requires adept technicians capable of discerning relevant indications from irrelevant ones. MT finds extensive application in the detection of metal cracking, weld verification, and stress corrosion cracking, thereby playing a critical role in ensuring the structural integrity and reliability of components within industrial settings.